License to open a university in Ukraine
Cost of services:
Reviews of our Clients
... our work on joint projects assured us of your high level of professionalism
Establishing universities in Ukraine isn't a daily occurrence. However, some occasional individuals aspire to contribute to the advancement of higher education. Here, they come face-to-face with the less common nature of this process, which is why not all legal professionals have real-world exposure to it.
Nonetheless, we possess a positive track record in establishing educational institutions in Ukraine, including universities. We not only facilitate the licensing process but also offer comprehensive legal, accounting, and personnel consulting at all stages of establishing and developing an educational institution after successfully obtaining the license. Many of our clients have already taken advantage of our service for obtaining educational licenses and the corresponding legal guidance. It's precisely because of this experience that we're ready to share valuable insights and outline the pertinent requirements for institutions of this kind.
What are the requirements set for universities in Ukraine?
A private university is always a distinct legal entity with its own charter. The charter is subject to a specific set of stipulations, both explicit and implicit. Notably, among the implicit requirements is an exclusive dedication to educational activities, even though this might not be specified in the bylaws. Moreover, there are no particular dictates about the legal and organizational structure of the entity that will secure the license and eventually function as the university. There are also no requirements regarding a minimum amount for the charter capital. Nevertheless, it's sensible to consider an amount beyond a mere 100 hryvnias, as this carries reputational weight. Additionally, such considerations could potentially impact matters like credit acquisition when necessary.
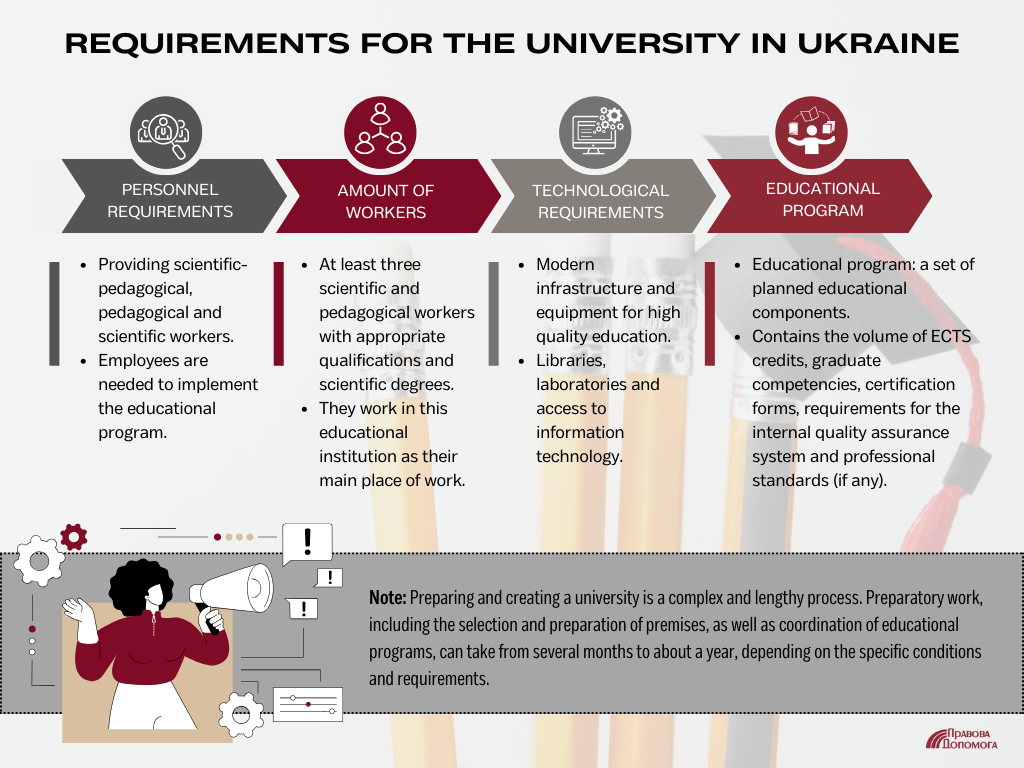
Personnel Requirements for a University
As the saying goes, "personnel make all the difference." This sentiment rings true in the context of higher education establishments. According to the licensing terms, an educational institution must have access to academic, pedagogical, and/or scientific personnel essential for executing the educational curriculum. Ultimately, everything centers around the nature of the educational program itself.
What should be the composition of employees holding academic degrees and/or scientific titles, and working at this institution as their primary place of employment? It should encompass at least 50% at the corresponding level of higher education or within the relevant educational program.
Among these employees, a segment consisting of individuals holding a Doctor of Science degree and/or the title of Professor should constitute:
- No less than 10%, if you intend to facilitate education at the second level of higher education (awarding Master's degrees; currently also encompassing Specialists).
- If you aspire to educate Doctor of Philosophy degree recipients (the third level of higher education and scientific research, postgraduate studies), there should be a minimum of two Doctor of Science degree holders.
What is a Doctor of Philosophy, and why is the term associated with philosophy? In many countries worldwide, this term is used for individuals who have conducted scholarly and academic research, defended their work, and published it in peer-reviewed publications. To put it simply, it's essentially equivalent to what was previously referred to as a "Candidate of Sciences." This term persisted from Soviet times until December 31, 2020. It was then replaced by a more universally recognized term. It's important to note that the term doesn't necessarily have a direct connection to philosophy. It's a designation used for scholarly professionals across various disciplines.
Number of Employees in the University
The institution must have no fewer than three academic staff members with the appropriate qualifications related to the educational program, possessing an academic degree and/or scientific title, and working at this institution as their primary place of employment.
These requirements are far from being an exhaustive list pertaining to personnel. The requirements have their own nuances based on specialties. Among other requisites, academic and pedagogical staff members should exhibit accomplishments within their professional domain, including:
- Having a minimum of five publications in recognized Ukrainian professional publications.
- Holding either one patent for an invention or five declarative patents for inventions or utility models, or possessing no fewer than five certificates of copyright registration for a work.
- Contributing to the creation of a published textbook, instructional material (including electronic versions), or a monograph.
- Defending a dissertation in pursuit of obtaining an academic degree.
There are several other criteria to consider.
Technological Requirements for University Licensing
Technological requirements can be divided into several categories:
- Facilities. The minimum area should be 2,000 square meters. This is a basic requirement, and without meeting it, there's no further discussion. Generally, the calculation for space is around 2.4 square meters per student, considering no more than three changes.
- Material and Technical Base. The institution must be equipped with classrooms, laboratories, workshops, gymnasiums, and sports facilities/stadiums as necessary to fulfill the educational program and curricula. Additionally, there should be a medical unit, a library with a reading hall, an auditorium or concert hall, and a dining facility.
At least 25% of instructional rooms should be equipped with multimedia technology. Computer equipment is allowed, provided it has a service life of no more than eight years.
Educational Program(s) for Specializations
An educational program constitutes a collection of meticulously planned educational elements designed to guide students towards achieving specific learning outcomes. The university's educational program should encompass:
- The allocation of ECTS credits (European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System) necessary to obtain the respective higher education degree.
- A roster of competencies that graduates are expected to possess.
- Assessment methodologies for educational candidates.
- Requirements for the internal quality assurance system pertaining to education.
- Adherence to professional standards, where applicable.
This succinctly outlines what prospective university founders should be prepared for. As practical experience has shown, the preparatory efforts entailing location selection, curriculum alignment, and program endorsement can extend for a notable duration – approximately a year.
Nevertheless, if you're steadfast in your determination and believe this endeavor to be essential, proceed resolutely towards your objective. We're here to gladly assist you, making your journey as concise and comfortable as possible.
You can find the cost of an Educational License for a university here.
You may also like the following topics:
Regulations and Expenses for Establishing a Private Kindergarten in Ukraine
How to Obtain a School License in Kyiv? Have the Requirements Altered Amidst the War?
Our clients