What is automatic tax information exchange and how does it work?
Cost of services:
Reviews of our Clients
Previously, the exchange of tax information was mainly regulated by separate articles of agreements aimed at avoiding double taxation, as well as the Convention on Mutual Administrative Assistance in Tax Matters (of which Ukraine is a participant), which were primarily limited to requests made by tax authorities. However, since 2017, there has been a worldwide implementation of the OECD Common Reporting Standard (CRS) which facilitates automatic exchange of tax information.
Financial institutions such as banks (excluding payment systems), financial brokers, and securities traders are required to report under this system.
Note: Registration agents who provide services to companies are not subject to the reporting requirements.
The financial information subject to automatic reporting is collected from personal accounts of individuals and corporate accounts of companies. Essentially, this system focuses on personal accounts of individuals opened outside of their country of tax residency, and corporate accounts of companies.
The information that will be exchanged pertains to the account balances at the end of the reporting year.
In practice, automatic exchange of information with regards to corporate accounts (of companies) works like this:
- The financial institution (bank) receives information from the taxpayer (company) and sends it to the tax authorities of its country;
- The tax authorities of the country where the financial institution (bank) is located sort the received information by the jurisdictions of the taxpayers and send it in encrypted form to the tax authorities of the taxpayers' country of residence;
- The tax authorities of the taxpayers' country of residence receive the information, decrypt it, and enter it into the local tax system;
- The tax authorities of the taxpayers' country of residence analyze the received data and take measures regarding the initiation of relevant tax procedures.
For example, if a Cypriot company has an account in a Latvian bank and has two owners (beneficiaries) from Russia and the UK, the Latvian tax authorities (having received information from the Latvian bank) will transmit the information on the results of the year to the countries of tax residence of the beneficiaries, i.e. Russia and the UK.
In our article, we explain how this works for Ukraine, what risks it poses, and what we propose to do about it. We highly recommend that those who plan to open a business abroad or relocate their business from Ukraine pay very close attention to this information.
You may also like: Where and How to Open an Account for Your Crypto Company?
Which countries automatically exchange tax information?
The standards have been implemented by practically all countries that are most frequently used when building tax optimization structures. Currently, over 100 countries, including all European countries, the United States, Russia, Asian countries, and others are participating in automatic exchange of tax information.
In Ukraine, the first data collection was supposed to take place in 2023, but it has been postponed (until the end of the war).
Ukraine and CRS in 2023
Ukraine has committed to implementing automatic exchange of tax information as part of the BEPS plan.
On November 3, 2022, the SFS, with the support of the Ministry of Finance, joined the Multilateral Competent Authority Agreement on Exchange of Country-by-Country Reports (MCAA ECCR). The goal of joining the agreement is for Ukraine to join the international system of automatic exchange of country-by-country reports, which has already been joined by over 90 countries worldwide.
Currently, the Ministry of Finance of Ukraine has developed a draft law of Ukraine "On Amendments to the Tax Code of Ukraine and some legislative acts of Ukraine on the implementation of the international standard for automatic exchange of information on financial accounts", which has already passed the first reading in the Verkhovna Rada.
MCAA ECCR will come into effect after the necessary legislation is passed to implement CRS, after compliance checks by the Global Forum, after ensuring that the tax authorities have the technical capability to exchange information, and after meeting other conditions.
The essence of automatic exchange of information is that, starting from the reporting year, information on foreign accounts held by Ukrainian tax residents (both individuals and legal entities) will be automatically transmitted to Ukraine. Conversely, the Ukrainian tax authority will send information on accounts held by non-residents (serviced by Ukrainian banks) to the countries where the account holders are tax residents.
According to the Draft Law and the Implementation Plan for CRS in Ukraine (developed by the Ministry of Finance), the first reporting period was supposed to start on January 1, 2023 and end on December 31, 2023. Therefore, the proper comprehensive checking procedures for identifying reportable accounts should be applied from January 1, 2023. The first exchange of tax information was supposed to take place in 2024. However, due to the ongoing conflict, the deadlines specified in the draft law are postponed until after the end of the war.
You may also like: Relocating Ukrainian IT Company in 2023
Why automatic exchange of tax information is necessary?
The automatic exchange of tax information is necessary to require banks to provide information about their clients to the tax authorities, in order to detect assets "hidden" by individuals and companies in foreign banks, both on personal and corporate accounts.
Once the automatic exchange is properly implemented in Ukraine, information about Ukrainians' personal accounts abroad, as well as about their companies' accounts, will become available to the Ukrainian tax authorities. Consequently, questions will arise about the source of the funds and the payment of taxes on them.
You may also like: Registering a Company in Poland
How to secure yourself and your assets abroad?
While automatic exchange of information is not yet fully operational in Ukraine, it's a good time to start thinking about:
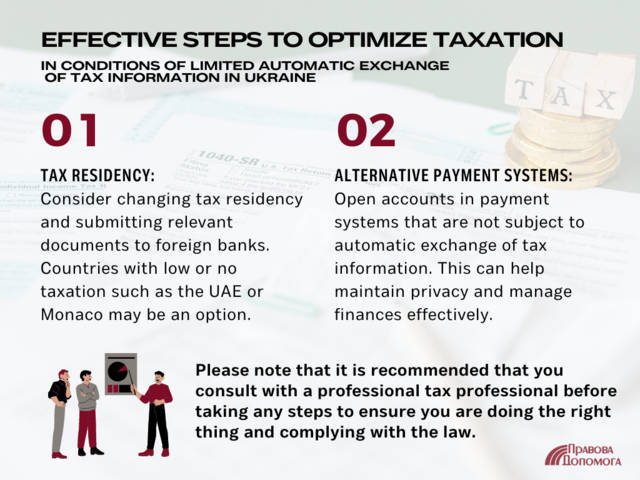
- Changing your tax residency and providing foreign banks with documents confirming your tax residency in countries like the UAE, Monaco, and other low-tax or tax-free jurisdictions. This will allow you to adjust the route of information transmission.
- Opening accounts in payment systems that do not exchange tax information, and more.
Our lawyers can offer:
- Analysis of assets (companies, personal accounts) to identify those at risk under CRS.
- Development of a plan of action aimed at minimizing risks under CRS.
- Planning for individual tax residency.
- Communication with foreign banks to plan documents that will be provided for individuals to confirm their tax residency.
- Restructuring ownership of foreign companies.
- Opening accounts in payment systems, and more.
Do you want to protect your assets in Ukraine and abroad? It's not a problem. Contact our specialists, and we'll find the optimal solution.
Check out the cost of tax optimization services here.
Find out more about relocating your business from Ukraine here.
Our clients